Q-SLICE Threat Harness v3 is a configurable testbed for simulating quantum adversarial scenarios. It builds on previous versions by introducing user‑input parameters so researchers can explore different environments and attack conditions without modifying the code. The harness integrates tests across eight threat vectors in the six Q-SLICE elements:
1. Quantum Exploitation (Grover, Shor)
2. Subversion of Trust (BB84, RNG bias)
3. Legacy Exploitation
4. Integrity Disruption (Bell states)
5. Coherence Attacks
6. Ecosystem Abuse
It also computes reproducible Q-SLICE metrics (depth, fidelity, leakage, bias, QBER). It enables organisations, researchers, and security leaders to:
- Model quantum adversaries: Formalise new classes of quantum‑enabled threats, from algorithmic collapse to entropy manipulation.
- Benchmark resilience: Measure post‑quantum security readiness using reproducible metrics such as fidelity, QBER, and entropy bias.
- Bridge research and practice: Translate complex quantum security results into actionable insights for operational risk frameworks.
- Support migration planning: Provide scenario‑based intelligence to guide cryptographic transition strategies and PQC adoption.
How It Works
Q‑SLICE integrates advanced quantum simulation, adversarial modeling, and operational taxonomy design into a unified harness:
- Scenario Engine: Generates adversarial models (e.g., Shor’s algorithm, RNG bias) to stress‑test cryptographic systems.
- Metric Dashboard: Produces clear, reproducible outputs—fidelity scores, error rates, and resilience KPIs—ready for examiner review or executive reporting.
- Adaptive Harness: Iteratively refines simulations with fallback logic (Aer/Statevector), ensuring reproducibility across environments.
- Operational Taxonomy: Maps quantum threat organisms into structured categories, aligning with industry standards and risk frameworks.
- Accessible Outputs: Converts technical results into plain‑language insights, making quantum security actionable for diverse audiences.
Quantum computing is rapidly reshaping the cybersecurity landscape. Traditional cryptographic systems face collapse under quantum algorithms, while new adversarial behaviors emerge. Q‑SLICE equips organizations with the tools to:
- Anticipate quantum‑driven risks before they materialise.
- Validate resilience against post‑quantum adversarial scenarios.
- Communicate results clearly to stakeholders, regulators and non‑specialist audiences.
- Shape the future of quantum security standards through reproducible, evidence‑based modeling.
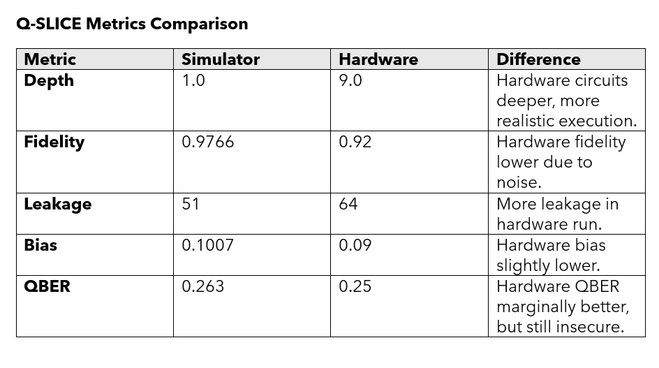
You can download the Q-SLICE threat model v3 for free from GitHub there is a (v1, v2 and v3) CLI, GUI and Dashboard version based on v3. complete with a user guide to help with interpreting results and building use cases. There is also v4 which is designed to run on IBM Quantum Cloud and does offer slightly different results being on real hardware and not a simulator as can be seen in the table below.
Link to: GitHub Q-SLICE Threat Harness
Link to: ORCID